A micro-ring resonator with big potential
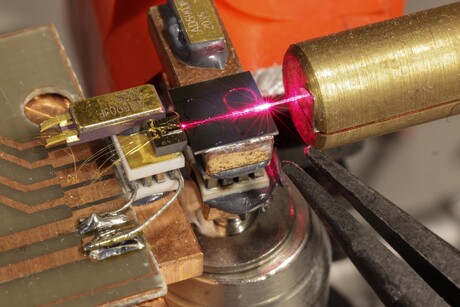
Researchers from EPFL’s Photonic Systems Laboratory (PHOSL) have developed a chip-scale laser source that enhances the performance of semiconductor lasers while enabling the generation of shorter wavelengths.
This pioneering work, led by Professor Camille Brès and postdoctoral researcher Marco Clementi from EPFL’s School of Engineering, represents a significant advance in the field of photonics, with implications for telecommunications, metrology and other high-precision applications.
The study, published in the journal Light: Science & Applications, reveals how the researchers, in collaboration with the Laboratory of Photonics and Quantum Measurements, have integrated semiconductor lasers with silicon nitride photonic circuits containing microresonators. This integration results in a hybrid device capable of emitting highly uniform and precise light in both near-infrared and visible ranges, filling a technological gap that has long challenged the industry.
“Semiconductor lasers are ubiquitous in modern technology, found in everything from smartphones to fibre optic communications. However, their potential has been limited by a lack of coherence and the inability to generate visible light efficiently,” Brès said. “Our work not only improves the coherence of these lasers but also shifts their output towards the visible spectrum, opening up new avenues for their use.”
Coherence, in this context, refers to the uniformity of the phases of the light waves emitted by the laser. High coherence means the light waves are synchronised, leading to a beam with a very precise colour or frequency. This property is crucial for applications where precision and stability of the laser beam are paramount, such as time keeping and precision sensing.
Increased accuracy and improved functionality
The team’s approach involves coupling commercially available semiconductor lasers with a silicon nitride chip. This tiny chip is created with industry-standard, cost-efficient CMOS technology. Thanks to the material’s low-loss properties, there is little to no light that is absorbed or escapes. The light from the semiconductor laser flows through microscopic waveguides into extremely small cavities, where the beam is trapped. These cavities, called micro-ring resonators, are intricately designed to resonate at specific frequencies, selectively amplifying the desired wavelengths while attenuating others, thereby achieving enhanced coherence in the emitted light.
The other significant achievement is the hybrid system’s ability to double the frequency of the light coming from the commercial semiconductor laser — enabling a shift from the near-infrared spectrum to the visible light spectrum. The relationship between frequency and wavelength is inversely proportional, meaning that if the frequency is doubled, the wavelength is reduced by half. While the near infrared spectrum is exploited for telecommunications, higher frequencies are essential for building smaller, more efficient devices where shorter wavelengths are needed, such as in atomic clocks and medical devices.
These shorter wavelengths are achieved when the trapped light in the cavity undergoes a process called all-optical poling, which induces what is known as second-order nonlinearity in the silicon nitride. Nonlinearity in this context means that there is a significant shift, a jump in magnitude, in the light's behaviour that is not directly proportional to its frequency, arising from its interaction with the material. Silicon nitride does not normally incur this specific second order nonlinear effect, and the team performed an elegant engineering feat to induce it: The system takes advantage of the light’s capacity, when resonating within the cavity, to produce an electromagnetic wave that provokes the nonlinear properties in the material.
An enabling technology for future applications
“We are not just improving existing technology but also pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with semiconductor lasers. By bridging the gap between telecom and visible wavelengths, we’re opening the door to new applications in fields like biomedical imaging and precision timekeeping,” said Marco Clementi, who played a key role in the project.
One of the most promising applications of this technology is in metrology, particularly in the development of compact atomic clocks. The history of navigational advancements hinges on the portability of accurate timepieces — from determining longitude at sea in the 16th century to ensuring the accurate navigation of space missions and achieving better geo-localisation today. “This significant advancement lays the groundwork for future technologies, some of which are yet to be conceived,” Clementi said.
The team’s understanding of photonics and material science could lead to smaller and lighter devices and lower the energy consumption and production costs of lasers. Their ability to take a fundamental scientific concept and translate it into a practical application using industry standard fabrication underscores the potential of solving complex technological challenges that can lead to unforeseen advances.
Feeling the future: wearable tech simulates realistic touch
Researchers from Northwestern University have developed a device that applies dynamic forces in...
Enhancing stability in bioelectronic materials for computing
Scientists from Rice University have streamlined the production of a material widely used in...
How AI is remodelling the IoT
Incorporating AI into the IoT will dramatically enhance its capability and flexibility. But...





