Enhancing supercapacitance in VGNs
Indian researchers have found a way to increase the supercapacitance of vertical graphene nanosheets (VGNs) — 3D networks of carbon nanomaterial that grow in rows of vertical sheets. Also known as carbon nanowalls or graphene nanoflakes, VGNs provide a large surface area that enhances charge storage capacity, promising use in energy storage systems, fuel cells, bio sensors, magnetic devices and more.
Supercapacitors are in many cases preferable to batteries, as they can store more energy and are able to charge faster — mainly due to the presence of VGNs. They are particularly advantageous in supercapacitor electrodes due to properties such as interconnected porous nanoarchitecture, excellent conductivity, high electrochemical stability and an array of nanoelectrodes. These advantages can be enhanced depending on how the material is grown, treated and prepared to work with electrolytes.
“Performance of a supercapacitor not only depends on the geometry of electrode material, but also depends on the type of electrolyte and its interaction with the electrode,” said Subrata Ghosh of the Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research at the Homi Bhabha National Institute. “To improve the energy density of a device, [electric] potential window enhancement will be one key factor.”
Modelling shows that VGNs should be able to provide high charge storage capabilities, and the scientific community is trying to unlock the key to reaching the levels of efficiency that are theoretically available. Required improvements include greater capacitance per unit of material, greater retention, less internal resistance and greater electrochemical voltage ranges (operating potential windows).
“Our motivation was to improve VGN performance,” Ghosh said. “We have taken two strategies. One is inventing a novel electrolyte, and another is improving the VGN structure by chemical activation. The combination of both enhances the charge storage performance remarkably.”
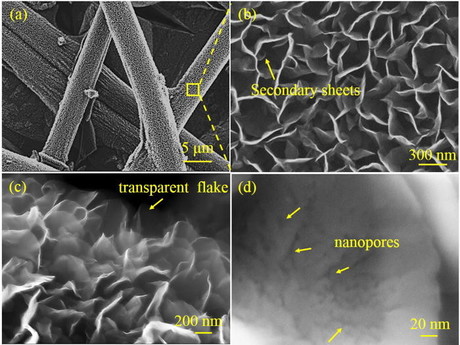
The researchers treated VGNs with potassium hydroxide (KOH) to activate the electrodes and then allowed the treated electrodes to interact with a hybrid electrolyte, testing the formation of the electric double layer at the electrode/electrolyte interface. They also examined the morphology, surface wettability, columbic efficiency and areal capacitance of VGN.
Published in the Journal of Applied Physics, the result was the creation of a hybrid electrolyte that combines the advantages of aqueous and organic electrolytes to increase supercapacitor performance of VGNs. Using an organic salt, tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate (TEABF4), in an acidic aqueous solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4), the researchers created an electrolyte that extended the device’s operating window.
“Aqueous and organic electrolytes are extensively used, but they have their own advantages and disadvantages,” noted Ghosh. “Hence the concept of hybrid electrolyte arises.”
Improvement of VGN architecture was associated with the process of KOH activation, which grafted the oxygen functional group onto the electrode, improved electrode wettability, reduced internal resistance and provided a fivefold improvement in capacitance of the VGNs. According to Ghosh, this activation approach can be applied to other supercapacitor devices that are based on nanoarchitecture.
Novel design for flexible thermoelectric semiconductor
Researchers have identified a new material which could be used as a flexible semiconductor in...
A lighter, smarter magnetoreceptive electronic skin
Researchers have developed an innovative e-skin that facilitates a new level of interaction...
Single transistor used to implement neuromorphic behaviour
Researchers have demonstrated that a single transistor can mimic neural and synaptic behaviours,...




