Borophene may be best for flexible electronics
US scientists have claimed that 2D materials like graphene may be too flat and hard to stretch to serve in flexible, wearable devices. The solution to this problem lies in a material called borophene.
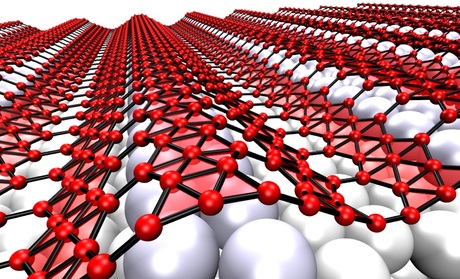
Theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson, from Rice University, and his team observed examples of naturally undulating, metallic borophene — an atom-thick layer of boron — and suggested that transferring it onto an elastic surface would preserve the material’s stretchability along with its useful electronic properties. Their research has been published in the journal Nano Letters.
Highly conductive graphene has promise for flexible electronics, Yakobson said, but it is too stiff for devices that also need to stretch, compress or even twist. But borophene deposited on a silver substrate develops nanoscale corrugations. Weakly bound to the silver, it could be moved to a flexible surface for use.
Rice collaborated with experimentalists at Argonne National Laboratory and Northwestern University to study borophene, which was made in small quantities. Under the microscope, borophene displays corrugations that demonstrate its wavy nature, meaning it can be highly stretched once removed from the substrate or reattached to a soft one, Yakobson said.
The group built computer simulations to analyse the properties of materials from the atoms up. Simulations by first author Zhuhua Zhang, a postdoctoral researcher in Yakobson’s group, showed that hexagonal vacancies in borophene help soften the material to facilitate its corrugated form.
“Borophene is metallic in its typical state, with strong electron-phonon coupling to support possible superconductivity, and a rich band structure that contains Dirac cones, as in graphene,” Yakobson said.
There is, however, a hitch: borophene needs the underlying structure to make it wavy. When grown on a featureless surface, its natural form resembles graphene, the flat, chicken-wire arrays of carbon atoms. Zhang said borophene is better seen as a triangular lattice with periodic arrays of hexagonal vacancies.
Borophene prefers to be flat because that’s where its energy is lowest, Yakobson said. But surprisingly, when grown on silver, borophene adopts its accordion-like form while silver reconstructs itself to match. The corrugation can be retained by ‘regluing’ boron onto another substrate.
“This wavy conformation so far seems unique due to the exceptional structural flexibility and particular interactions of borophene with silver, and may be initially triggered by a slight compression in the layer when a bit too many boron atoms get onto the surface,” Zhang said.
A lighter, smarter magnetoreceptive electronic skin
Researchers have developed an innovative e-skin that facilitates a new level of interaction...
Single transistor used to implement neuromorphic behaviour
Researchers have demonstrated that a single transistor can mimic neural and synaptic behaviours,...
Novel fabrication technique for flexible electronics
Researchers have harnessed nature's intrinsic hierarchical fractal structures to improve the...





