Spinning around: unlocking the potential of kagome metallic crystal

A global team of researchers, co-led by a City University of Hong Kong (CityU) physicist, has found that a novel metallic crystal displays unusual electronic behaviour on its surface, due to the crystal’s unique atomic structure.
The research findings open up the possibility of using this material to develop faster and smaller microelectronic devices.
The material that was studied is a recently discovered “kagome” metal compound that consists of three elements: gadolinium (Gd), vanadium (V) and tin (Sn), and is classed as a “1-6-6” material to indicate the ratio of the three metal elements present in the GdV6Sn6 crystal. The atoms are arranged in a complex but regular geometric pattern, resulting in interesting surface characteristics. Normally, negatively charged electrons in atoms move within discrete energy bands at different distances from the positively charged nuclei. However, on the surface of the GdV6Sn6, top layers of exposed atoms are predicted to interact with each other and deform the topology (that is, the shape and positioning) of the energy bands. In theory, this deformation could introduce a new and stable electronic property that has reportedly not been detected in GdV6Sn6 or any other kagome metal.
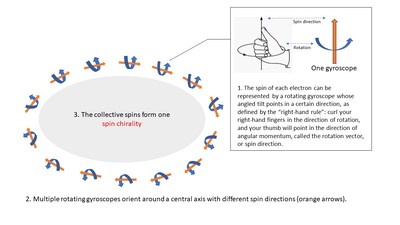
Dr Ma Junzhang, Assistant Professor in the Department of Physics at CityU, said that the team of researchers observed that a kagome metal can exhibit altered electronic energy-band structures of the type known as ‘topologically non-trivial Dirac surface states’. “Because of their intrinsic spin and charge, electrons create their own magnetic field and behave like tiny gyroscopes that have both rotation and an angled tilt that points in a certain direction. We demonstrated that in GdV6Sn6, the surface electrons become reordered or ‘spin-polarised’, and their tilts reorient themselves around a common axis that is perpendicular to the surface,” Junzhang said.
The ordered orientation of electrons around a shared axis is their ‘spin chirality’, which can be in either a clockwise or an anticlockwise direction (as demonstrated in Figure One). The research team was also able to successfully reverse the spin chirality by performing a simple physical modification of the crystal surface. “Because we found that the spin chirality of the spin-polarised electrons is easily reversible, our material has great potential for application in next-generation transistors in the field of spintronics,” Junzhang said.
The study, published in Science Advances, was driven by theoretical predictions of novel surface electronic band structures after considering special features of GdV6Sn6 kagome crystals. For example, layers of repeating V3Sn subunits are stacked between alternating layers of Sn and GdSn2 (as demonstrated in Figure 2(i)). Furthermore, multiple V3Sn subunits are arranged geometrically in a “kagome layer”, whose repeating pattern of six equilateral triangles surrounding a hexagon resembles the kagome lattice seem in Japanese bamboo basket weaving (as shown in Figure 2(ii)). The V3Sn kagome layer is non-magnetic, whereas the GdSn2 layer is magnetic.

First, the researchers made GdV6Sn6 crystals by heating Gd, V and Sn metals and slowly cooling the product. Then, after confirming the chemical composition and structure by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, they cleaved a crystal through the stacked layers and analysed the exposed surface by angle-resolved photoemission, spectroscopy or ARPES. The results revealed that the cleaved surface possessed reshaped energy band structures, and further analysis demonstrated clockwise spin character. The researchers also showed that the surface energy bands could be warped drastically by coating the surface with potassium atoms, in a process known as electron doping. As a result, the electron spin chirality switched from clockwise to anticlockwise with increasing doping level (Figure 3).

The ability to deliberately reserve the spin chirality of surface electrons on the GdV6Sn6 crystal makes it a promising candidate material for numerous practical electronic applications. Junzhang suggests that in the future, researchers may be able to apply a local voltage, or electrostatic ‘gate’, to directly manipulate or tune the electronic band structure and hence alternate the electron spin chirality on the surface of 1-6-6 kagome metals. “Controlling the direction of spin-polarisation of electrons is an attractive alternative to traditional binary digital coding based on the presence or absence of electrical charge, which is relatively slow and can lead to problems such as device heating. Our technology could significantly increase efficiency in digital information transfer, with less heat generation, and could ultimately be exploited in quantum computing when coupled with superconductors,” Junzhang said.
The first authors of the study are Dr Hu Yong from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Switzerland, and Dr Wu Xianxin from the Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing. The corresponding authors are Dr Hu, Dr Ma from CityU and Professor Shi Ming from the PSI. Collaborators included Professor Xie Weiwei from Rutgers University, US, who provided the samples, and Professor Andreas Schnyder from the Max Planck Institute, Germany.
3D-printed, shape-shifting antenna inspired by sci-fi
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, have created an...
Researchers knit 'blanket' of radio-frequency antennas
Researchers have used traditional flat-knitting techniques to fabricate flexible and lightweight...
Unlocking next-gen chip efficiency
By studying how heat moves through ultra-thin metal layers, researchers have provided a...




